Types of Hair Loss Treatments | Latest and Most Effective Methods

- Latest and Most Effective Hair Loss Treatment Methods at a Glance
- 1. Oral and Topical Drug Treatments (Minoxidil, Finasteride)
- 2. Advanced Clinical Treatments for Hair Regrowth
- 3. Hair Transplant: The Definitive Solution for Baldness and Low Density
- Before Treatment: Common Causes of Hair Loss and How to Diagnose
- 4. Home Remedies and Methods for Prevention and Control of Hair Loss
Hair loss (alopecia) is one of the most common health and aesthetic concerns, affecting millions worldwide. Whether it is hereditary, caused by stress, nutritional deficiencies, or hormonal problems, finding the best hair loss treatment method is essential for achieving desired density and preventing baldness. This article is a comprehensive and specialized guide that introduces you to the most effective and latest types of hair loss treatments, from pharmaceutical therapies to clinical procedures and surgery.
Latest and Most Effective Hair Loss Treatment Methods at a Glance
To quickly address user needs and view a summary of treatments, please check the table below:
| Treatment Method | Primary Mechanism | Common Uses | Overall Conclusion |
| Minoxidil (Topical) | Vasodilator, prolongs the growth phase (Anagen) | Male and female pattern hair loss | Most effective over-the-counter treatment; requires continuous use. |
| Finasteride (Oral) | Inhibitor of the DHT hormone | Male pattern hair loss (Androgenetic Alopecia) | Most widely used oral drug; requires a doctor’s prescription. |
| PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) | Injection of activated platelets containing growth factors | Strengthening weak follicles, diffuse hair loss | Minimally invasive clinical procedure; enhances hair growth. |
| Mesotherapy | Injection of vitamin and medicinal cocktails | Deep scalp nourishment, stress-related hair loss | Supplements other treatments; improves scalp environment. |
| Hair Transplant (FIT/FUT) | Grafting follicles from the donor area | Complete baldness, receding hairline, low density | Definitive and permanent solution for areas without hair. |
1. Oral and Topical Drug Treatments (Minoxidil, Finasteride)
Pharmaceutical treatments are the first line of defense against hair loss. These methods are particularly effective for treating male pattern hair loss (Androgenetic Alopecia) and certain types of diffuse hair loss.

Minoxidil: Mechanism of Action, Dosage, and Side Effects
Minoxidil is a topical medication originally developed to treat high blood pressure, but its side effect of stimulating hair growth was discovered. Its exact mechanism is not fully understood, but it is believed to improve blood flow to the hair follicles by widening blood vessels, delivering more oxygen and nutrients, and prolonging the hair’s growth phase (anagen).
- How to Use: Typically applied as a 2% or 5% solution or foam, twice daily, on the affected area.
- Side Effects: The most common side effects include scalp irritation, itching, and, in rare cases, unwanted hair growth in other areas (hypertrichosis).
read more: 7 of the Best Herbal Teas for Hair Loss
Finasteride and Spironolactone: Anti-Androgen Medications
Finasteride is an oral drug typically prescribed only for men with hereditary pattern hair loss. It works by inhibiting the 5-alpha reductase enzyme, which reduces the conversion of the testosterone hormone into Dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT is the main culprit in miniaturizing hair follicles in genetically predisposed men.
- Spironolactone: This is also an anti-androgen often used to treat female pattern hair loss that has not responded to topical treatments or is caused by Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS).
- Expert Note: Anti-androgen treatments are highly effective but require a doctor’s prescription and careful monitoring of the individual’s overall health status.
Essential Vitamin and Mineral Supplements to Stop Hair Loss
Hair loss can be a sign of nutritional deficiencies. Taking the right supplements can help strengthen hair follicles and prevent further loss.
- Biotin (Vitamin B7): One of the most important vitamins for producing keratin, the main protein component of hair.
- Vitamin D: This vitamin plays a key role in the hair growth cycle, and its deficiency can lead to Telogen Effluvium (diffuse hair loss).
- Iron and Ferritin: Iron deficiency anemia is one of the most common causes of hair loss in women.
- Zinc: This mineral is involved in hair tissue repair and follicle growth, but high doses can paradoxically cause hair shedding.
2. Advanced Clinical Treatments for Hair Regrowth
When medications and supplements alone are insufficient, or to enhance their effect, advanced clinical procedures come into play.

Hair Mesotherapy: Injecting Growth Cocktails into the Scalp
Mesotherapy involves injecting micro-doses of vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and sometimes minoxidil into the middle layer of the scalp (mesoderm). The goal is to provide immediate, direct nutrition to the hair follicles and improve localized blood circulation.
Hair PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma): Using Activated Blood Platelets
PRP is a regenerative method where a sample of the patient’s own blood is drawn, and then the platelet-rich plasma is separated by centrifugation. This plasma contains high levels of growth factors, which, upon activation and injection into the scalp, stimulate stem cells, prolong the hair growth phase, and increase the thickness of fine hairs.
Microneedling and Carboxytherapy: Stimulating Scalp Collagen Production
- Microneedling: Uses devices with very fine needles to create controlled micro-injuries on the scalp surface. This action aids in better absorption of topical medications and stimulates the production of collagen and elastin in the scalp.
- Carboxytherapy: Involves injecting carbon dioxide (CO2) beneath the scalp to increase localized blood flow. The body responds to this CO2 increase by directing oxygen-rich blood to the area, leading to better follicle nourishment.
Expert Note (with English Paragraph and Translation):
“Advanced hair restoration techniques like PRP leverage the body’s intrinsic healing mechanisms. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor (PDGF) and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) are crucial proteins released by activated platelets. These factors signal the dermal papilla cells to enter the anagen phase (growth phase), leading to improved hair density and shaft caliber.”
Source: J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014 Mar;7(3):27-38.
3. Hair Transplant: The Definitive Solution for Baldness and Low Density
For individuals who have reached complete baldness or whose hair density has decreased too much to be compensated by non-invasive treatments, hair transplantation is the only definitive and permanent solution.
Comparing Hair Transplant Methods (FIT, FUT, SUT)
| Method | Mechanism | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| FUT (Strip Harvesting) | Removing a strip of skin containing follicles from the back of the head, then dissecting the units under a microscope. | Highest number of grafts, cost-effective. | Creates a permanent linear scar, longer recovery period. |
| FIT/FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) | Removing single follicular units using small punches. | No linear scar created, shorter recovery period. | Time-consuming procedure, limit on the number of grafts in one session. |
| SUT (Sequential Unit Transplantation) | A type of FUE performed with semi-automated devices. | Faster speed than traditional FUE, less damage to grafts. | Dependency on the skill and equipment of the surgical team. |
Post-Transplant Care and Recovery Period
The success of a hair transplant depends as much on the procedure itself as on the post-operative care. In the first few weeks after the transplant, the following should be avoided:
- Rough washing of the scalp.
- Exposure to direct sunlight.
- Strenuous physical activity and excessive sweating.
- Smoking and alcohol consumption, which can slow down the healing process.
Note: Shock shedding in the first month is normal; the transplanted hairs fall out so the follicles can enter the resting phase, after which permanent hair growth begins.
Before Treatment: Common Causes of Hair Loss and How to Diagnose
Choosing an effective hair loss treatment is only possible after accurately diagnosing the underlying cause of the shedding.
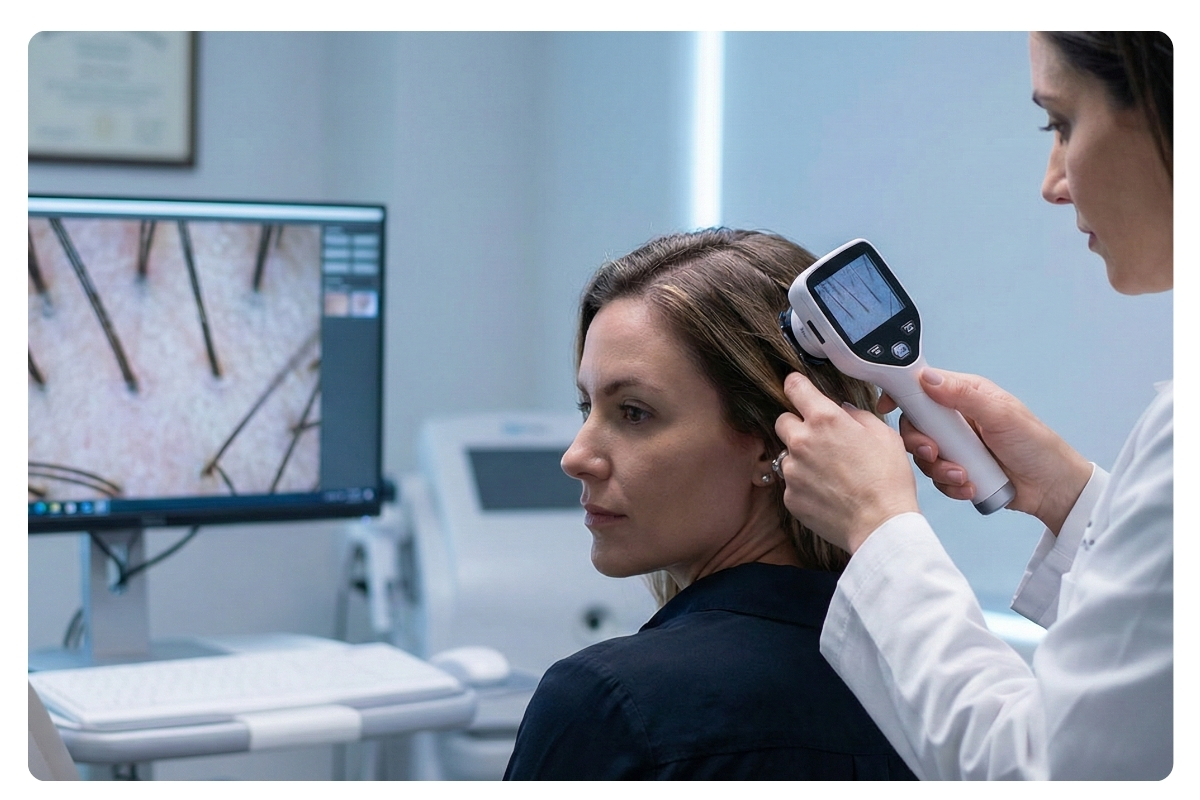
Hereditary Hair Loss (Androgenetic Alopecia) and Alopecia Areata (Patchy)
- Androgenetic Alopecia: The most common cause of hair loss, resulting from follicle sensitivity to the DHT hormone. In men, it presents as a receding hairline and baldness at the crown; in women, it appears as diffuse thinning on the crown.
- Alopecia Areata (Patchy): An autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, causing hair to fall out in circular patches.
Hair Loss Due to Vitamin Deficiency and Hormonal Problems (Thyroid, PCOS)
- Thyroid: Hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism can disrupt hormonal balance, leading to diffuse hair loss and dry hair.
- PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome): In women, PCOS causes increased production of androgens, resulting in male-pattern hair loss, unwanted hair growth (hirsutism), and acne.
Do Stress and Poor Diet Cause Hair Loss?
Yes. Severe and prolonged stress (especially intense physical stress such as surgery, high fever, or very restrictive diets) can lead to a condition called “Telogen Effluvium.” In this condition, a high percentage of hairs prematurely enter the resting phase, and severe shedding is observed within 3 to 6 months. Diets lacking in protein, iron, and B vitamins can also directly affect hair health.
4. Home Remedies and Methods for Prevention and Control of Hair Loss
Home remedies, alongside clinical and pharmaceutical treatments, significantly contribute to maintaining overall hair health and controlling shedding.

Best Diet and Necessary Supplements for Hair Strengthening
For healthy hair, your diet should include high-quality proteins (like lean meat, fish, legumes), Omega-3 fatty acids (like salmon, flaxseeds), and B vitamins.
| Important Nutrient | Reason for Importance |
| Protein | Primary building block of hair (keratin) |
| Iron | Carries oxygen to the follicles |
| Omega-3 | Reduces scalp inflammation and improves the growth environment |
| Biotin (in eggs and nuts) | Strengthens hair structure and prevents breakage |
read more: 7 of the Best Herbal Teas for Hair Loss
Correct Washing and Combing Techniques to Prevent Damage
- Washing: Use a mild, sulfate-free shampoo, gently massage the scalp (instead of vigorous scrubbing), and avoid extremely hot water.
- Combing: When wet, comb hair carefully with a wide-toothed comb, starting from the tips and moving toward the roots, to prevent tension and breakage. Minimize the continuous use of high heat (blow dryers and straighteners).
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Treatment Method Based on Hair Loss Type
Selecting the types of hair loss treatments must be a personal decision based on consultation with a dermatologist or hair specialist. For hereditary hair loss (androgenetic), medications like Minoxidil and Finasteride are the first line of treatment. For strengthening fine hair and improving the scalp environment, clinical methods such as PRP and Mesotherapy are recommended. Finally, hair transplantation is the ultimate solution for permanently restoring density in bald areas.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Is my hair loss permanent or temporary?
It depends on the cause. Hereditary hair loss (androgenetic) is permanent and requires continuous treatment, while hair loss due to stress or nutritional deficiency (Telogen Effluvium) is temporary and reversible once the cause is resolved.
2. How long does Minoxidil treatment take to show results?
To see significant results from Minoxidil, it must be used continuously for at least 3 to 6 months, and discontinuing it can lead to the recurrence of hair loss.
3. Is Finasteride safe for women to use?
No, Finasteride is usually contraindicated for pregnant women or women of childbearing age due to the risk of birth defects; however, it is sometimes prescribed in low doses for postmenopausal women.
4. For which type of hair loss is PRP most effective?
PRP is particularly effective for strengthening fine and weak hair in both male and female pattern hair loss, as well as reinforcing follicles after a hair transplant.
5. Does a hair transplant guarantee that my hair won’t fall out again?
The transplanted hairs, taken from the resistant donor area (back of the head), are permanent; however, the shedding of the individual’s original, non-transplanted hair may continue and requires supportive treatments.
6. Is Mesotherapy better than PRP?
PRP contains the individual’s own growth factors and is generally considered more potent than mesotherapy cocktails for stimulating hair growth and thickness.
7. Can stress cause complete baldness?
No, severe stress usually causes Telogen Effluvium (diffuse shedding) but does not directly lead to complete male or female pattern baldness.
8. What is the best time to start drug treatment?
The best time is as soon as abnormal thinning or hair loss is noticed, as treatment is most effective in the early stages of hair loss.
9. What are the common side effects of Finasteride in men?
The most common side effects include decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and, in rare cases, breast enlargement (gynecomastia).
10. What factors determine the cost of a hair transplant?
The cost depends on various factors, including the method of transplantation (FIT, FUT), the number of grafts required, the experience of the medical team, and the clinic’s geographical location.









Be the first to comment!